A New Age in Modern Drug Development
The foundational approach to modern medicine has remained the same since the earliest success of anti-infective medicines. It is built on the “target-first” principle of “discover disease causing agent” and “design drug that inhibits it most effectively”. Fast forward to today, several therapeutic modalities have been introduced (small molecules, monoclonals, ADC, RNA, etc.), and disease conditions have been treated. The methodology involved in alleviating the burden of chronic human diseases impacting large populations requires large, long, and narrowly focused developmental trials. The modern approach fundamentally focuses on target discovery-based medicine; it has an extremely high failure rate and unclear understanding of diseases within the context of overall human biology. Target discovery-based drug development takes over a decade to reach clinical approval and is an unpredictable and failure-prone process, which ultimately leads to slower and more costly drug development. We, at Unravel Biosciences, have disrupted this model through our Predictable Medicine™ innovation stack in powerful ways with extremely compelling human evidence.
The Predictable Medicine™ innovation stack is a tool that Unravel utilizes throughout drug development to clinically derisk drug targets, mechanisms, and therapeutics.
RNA: We analyze RNASeq data to give dynamic insights into a patient’s state of health. The transcriptome reflects the interactions between a patient’s genome, the environment, and time.
Rarify™: Our growing data-mine, Rarify™, contains 2600+ patient and control RNAseq data that we use as the building blocks for our disease models, Living Molecular Twins.
Non-invasive sampling modality: Though our Living Molecular Twins can be generated using any RNAseq dataset, a key component to our rapid and accessible insights are our non-invasive sampling modality, nasal swabs.
BioNAV™: BioNAV™ is our proprietary computational platform that assesses patient and control RNA against drug-gene interactions and perturbations to identify effective treatments for patients. It is the tool that simulates our Living Molecular Twins.
SquishyWare™: Our in vivo model, SquishyWare™ is a tool that can act as a stepping stool from in silico predictions to clinical translation, when necessary. It allows us to rapidly develop and characterize in vivo models to validate drug predictions for safety, efficacy, and toxicity.
Everyone has different experiences with drugs in terms of therapeutic outcome as well as side-effects. Rare pediatric conditions present an extreme case of this spectrum due to the complexity of developing biology, both in terms of efficacy and safety signals, and even more acute is the limited number of patients. We therefore started with a comprehensive assimilation of biological functions and building a combinatorial linked and validated network state of human health, in many ways, an in-silico representation of a “living molecular twin”. This is our foundation!
Our model has been built over a decade in association with the Wyss Institute at Harvard University, using over 40,000 molecular perturbations, with 121 million drug-gene interactions encompassing 364 million network patterns. In other words, we built a biological equivalent of testing 40,000 molecules on any patient.
We can therefore engineer medicines based on function, or lack of it, for any and every human condition. In essence, it is a patient-first approach to engineering therapies. Let us illustrate this through three powerful clinical challenges of high unmet need.
Case Study 1:
Leigh Syndrome, a rare and complex mitochondrial condition caused by ~110 genes. It impacts 1 in 40,000 children being diagnosed before three years old with no clear treatment [1].
The Cure Mito Foundation partnered with Unravel Biosciences to rapidly identify the minimum number of therapeutic interventions to treat all children with Leigh Syndrome. We utilized multiple elements of our innovation stack (nasal swabs, RNAseq protocol, BioNAV™ -- an AI/ML-based causal network biology engine) to identify three patient subgroups corresponding to potential drug candidates and response markers. The study analyzed 22 patients and 22 controls within three months due to the depth of our datamine (RARIFY™). The recommendations had a high degree of clinical certainty, enabling the Cure Mito Foundation to offer immediate therapeutic intervention for a few families and launch drug development programs for others.
Case Study 2:
We have performed several “proof-concept" studies to demonstrate acceleration and confidence in our approach.
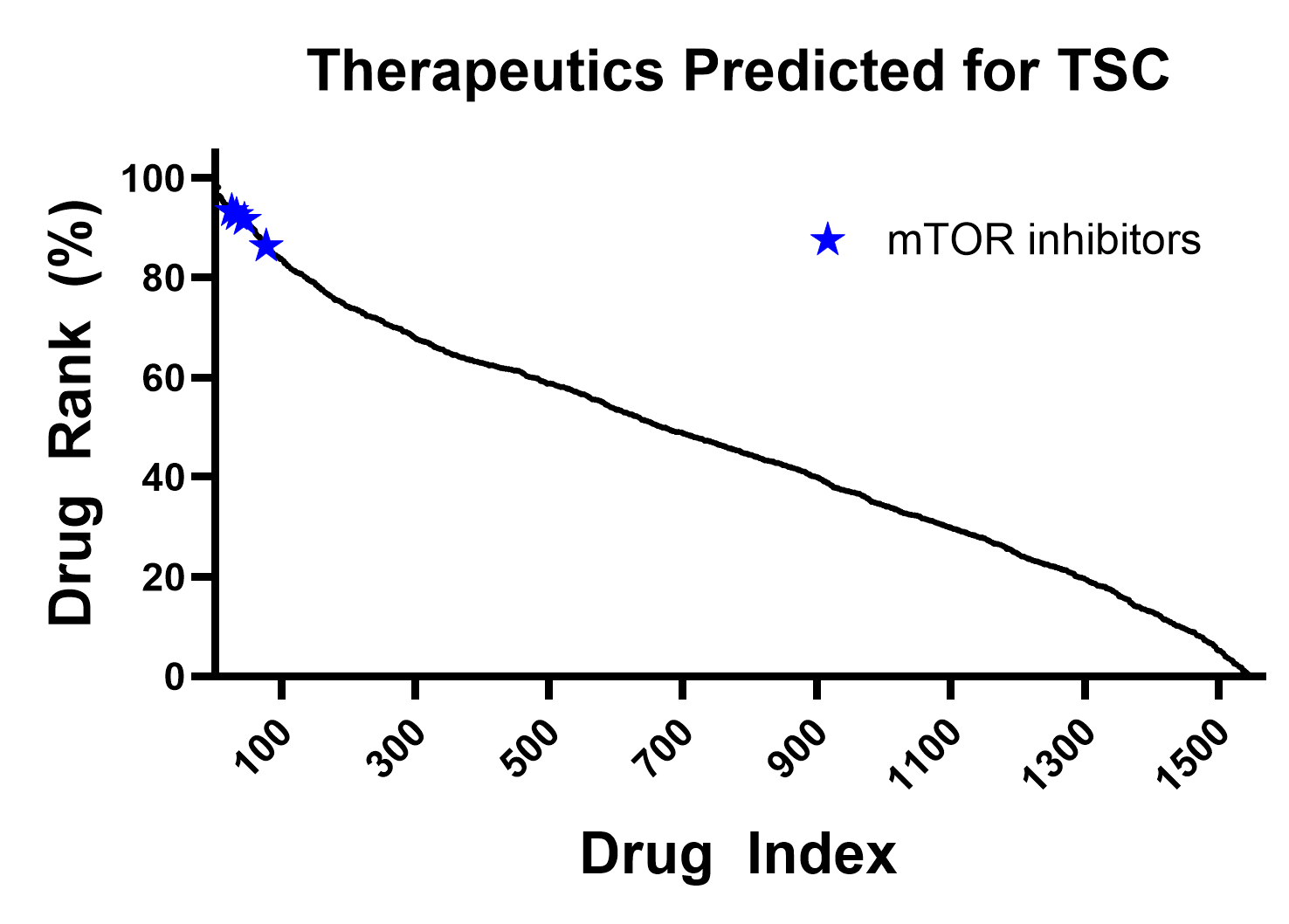
Using only the RNAseq data from 10 patient-derived Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC) organoids and their controls, BioNAV™ predicted a list of drug candidates for the treatment of TSC. The molecules in the top 5% of the predictions were primarily mTOR inhibitors, molecules that are considered the standard of care of TSC. In just two hours, BioNAV™ was able to recapitulate clinically validated mechanisms that took 25 years to develop after its discovery [2].
Figure: mTOR inhibitors, clinical standard of care for TSC, were predicted in the top 5% of molecules to treat TSC, demonstrating the ability to uncover effective therapeutic mechanisms with a target-agnostic platform.
Using high density gene expression and the BioNAV™ platform, therapeutic engineering can be accelerated by order of magnitude. In this specific case, it was 1,000x! This implies superior therapeutic agents can be introduced at a faster rate with a higher probability of success in clinical trials coming from mechanistic understanding of patients.
Case Study 3:
Rett Syndrome has one existing approved treatment, which, while effective in some patients, is ineffective in others or produces unbearable gastrointestinal side effects, making the drug a poor therapeutic option for many Rett patients [3].
Using the entirety of our innovative stack (i.e. BioNAV™, nasal swabs, in-vivo models, RARIFY™); we took one patient’s data and rapidly discovered anecdotal validation of vorinostat’s effectiveness in treating Rett Syndrome. We moved into animal studies, observed repeatability of therapeutic evidence, and transitioned into IND enabling human studies for Rett Syndrome [3]. Similar discoveries were made with everolimus (and many more therapeutic agents) over a 10-year period resulting in eventual approval for TSC. Utilizing an engineering approach, we have executed this in 18 months.
Case Study 4:
During the COVID-19 pandemic, several studies reported that statins reduced mortality in COVID-19 patients [4]. Using RNASeq data from 4,000 COVID-19 patients who were treated with statins, Unravel’s BioNAV™ platform predicted the expected outcomes of their treatment. Compared with the actual outcomes, Unravel predicted the different statins’ efficacies with 80% accuracy and demonstrated that, despite their shared mechanisms, some drugs within the statin class were more effective at treating COVID-19, while others were not [4]. This work was reflective of Unravel’s network approach to health where multiple therapeutic mechanisms may be necessary to treat complex disorders. Single drug targets, such as the statins’ shared target, are an incomplete approach to health. BioNAV™ was able to assess these drug-specific mechanisms in addition to the known mechanisms of the statin drug class with accuracy [4].
Case Study 5:
Breast cancer patients are very heterogeneous and, as in any disorder, respond to therapies differently with responders and nonresponders. This includes responses to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC). To avoid unnecessary side effects and further psychological stress for patients, a better understanding of the patient population is needed to determine which patients are good candidates for NAC [5].
Unravel took patient data from five public datasets and used BioNAV™ to stratify patients into responders and nonresponders to NAC. BioNAV™’s expected outcomes had 82.4% accuracy in comparison to actual patient outcomes. This was 12.9% and 18.6% more accurate than leading AI models [5].
Unravel Biosciences’ innovation stack of Predictable Medicine™ is clinically validated and can be applied with rapid flexibility across the drug development continuum. We are inviting patient families, foundations, and biotech to embrace a paradigm transforming approach to bringing impactful therapies to the clinic.
Authorship
This white paper was authored by Richard Novak, Frederic Vigneault, Mikayla Reitsma, and Aruzhan Bekbolatova.
References
[1] “About Leigh syndrome,” Cure Mito Foundation, https://www.curemito.org/about-leigh-syndrome/ (accessed Nov. 25, 2025).
[2] D. M. Sabatini, “Twenty-five years of mtor: Uncovering the link from Nutrients to growth,” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 114, no. 45, pp. 11818–11825, Oct. 2017. doi:10.1073/pnas.1716173114
[3] R. Novak et al., “Ai-enabled drug prediction and gene network analysis reveal therapeutic use of vorinostat for rett syndrome in preclinical models,” Communications Medicine, vol. 5, no. 1, Jul. 2025. doi:10.1038/s43856-025-00975-8
[4] M. M. Sperry et al., “Target-agnostic drug prediction integrated with medical record analysis uncovers differential associations of statins with increased survival in COVID-19 patients,” PLOS Computational Biology, vol. 19, no. 5, May 2023. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011050
[5] R. Flores, R. Nihalani, S. Umur, F. Vigneault, and R. Novak, Drug-gene network signature modeling predicts breast cancer patient response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy, Mar. 2025. doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-6130021/v1
©Unravel Biosciences 2025 | Contact@unravel.bio
| BioNAV™, RARIFY™, Predictable Medicine™ are exclusive trademarks of Unravel Biosciences |